- Home
- /
- Media & Entertainment
- /
- 3ds Max Forums
- /
- 3ds Max Ideas
- /
- [Primitives] Add Extra Standard and Extended Primitives for Mechanical, Piping, Jewelry, Abstract, V...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report
[Primitives] Add Extra Standard and Extended Primitives for Mechanical, Piping, Jewelry, Abstract, Visualization modeling purposes etc.
[Primitives] Add Extra Standard and Extended Primitives for Mechanical, Piping, Jewelry, Abstract, Visualization modeling purposes etc.
BOLT
Parameters: Presets: M10, M12.... etc. ; Model: Bolt, Nut; Bit: Type: None, Allen, Phillips; Depth, Flat Distance; Head: Type: Hex, Cap, Dome, Pan, Counter Sink; Flat Distance; Shank: Length, Diameter; Thread: Length, Major Diameter, Minor Diameter, Pitch, Crest Percent, Root Percent, Div Count.
GEAR
Parameters: Number of Teeth, Radius, Width, Base, Dedendum, Addendum, Pressure Angle, Skewness, Conical Angle, Crown.
GEAR WORM
Parameters: Number of Teeth, Number of Rows, Radius, Row Height, Dedendum, Addendum, Pressure Angle, Skewness per Row, Crown.
DIAMOND
Brilliant
Parameters: Segments, Table Width, Crown Height, Girdle Height, Real Girdle, Smooth Girdle, Pavilion Depth, Upper Facet Factor, Lower Facet Factor, Culet Size, Retain Angle of Pavilion Facets (if Cullet >0)
Diamond
Parameters: Segments, Girdle Radius, Table Radius, Crown Height, Pavilion Height
Gem
Parameters: Segments, Radius, Table Radius, Table Height, Pavilion Height.
PIPE JOINTS
Parameters: Radius, Divisions, Angle (per Arm if the case), Length Start, End Length, Arm Length (per Arm if the case), Number of Arms(For N-Joint type).
BEAMS
The default Max Beam like primitives lack some extrusion types and a Taper Parameter.
DISC
Creates a flat, filled circle with varying edge patterns. Parameters:
SUPERTOROID
Parameters: Big Radius, Small Radius, U-Segments, V-Segments, Ring Manipulator, Cross Manipulator.
STEP PYRAMID
Parameters: Number of Sides, Number of Steps, Initial Width, Height, Reduce Step by.
HONEYCOMB
Parameters: Number of Rows, Number of Coils, Cell Diameter, Edge Width.
STAR
Parameters: Points, Outer Radius, Inner Radius, Height
STUDIO BACKDROP
Ability to quickly create a flexible parametrical backdrop object for your visualizations. C4D recently introduced one as an capsule object asset in their Asset Browser with some handy parameters like overhanging, tilt, drop and some UV options like Fit mode (Fill, Contain, Cover, Custom Tile size) (link to video).
MENGER SPONGE
Parameters: Level, Width
QUAD CAPSULE
As opposed the default Capsule in 3ds Max, this capsule variant has quad caps.
TWISTED TORUS
The default Twist parameter for Torus primitive in Max produce undesirable results.
SUPER SHAPES
In Autodesk Maya Super shapes are primitives of highly mathematical nature based on cubes and spheres that are capable of creating complex organic shapes. In 3ds Max the closest thing we have is the RingWave under Extended Primitives. Possible Parameters:
Primary Parameters
Shape: Determines the base shape. Options include Super Ellipse, Spherical Harmonics, and Ultra.
Radius: Determines the size of the primitive based on the distance from its center to its pole.
Horizontal Divisions, Vertical Divisions: The number horizontal and vertical subdivisions (per quadrant) on the base mesh.
Create UVs: Determines how default UVs are created for the primitive. Options include None, Pinched at Pole, and Sawtooth at Pole.
Random: Generates a primitive of the current Shape with random attributes. Useful for quickly creating interesting start points.
Reset: Sets all attributes back to their default values for the chosen Shape.
Helix
This section is common to all super shapes and allows you to form the geometry into a spiral shape before applying their respective super shape properties. Parameters:
Merge Vertices: Merges the vertices on each end of the helix. If enabled, the rest of the Helix attributes won't have any effect.
Horizontal Revolutions: Determines the number of spirals.
Vertical Revolutions: Determines the fullness of the coil.
Vertical Offset: Determines the stretch of the coil.
Internal Radius: Determines the diameter of the inner coil.
X Offset, Z Offset: Offsets the coil's scale in the respective direction.
Super Ellipse
A Super Ellipse generates primitives using an exponential equation along x and y, resulting in arcs or inverse arcs along each axis. Specific Parameters:
V Exponent: Controls the exponent used to calculate the parabolic arc along the vertical.
H Exponent: Controls the exponent used to calculate the parabolic arc along the horizontal.
Mirror: Forces the H Exponent to match the V Exponent.
Spherical Harmonics
Spherical Harmonics apply a series of frequency equations to the surface of a sphere, resulting in pulsing topology.
V multiplier, V exponent: Controls the mathematical variables used to determine the shape along the vertical.
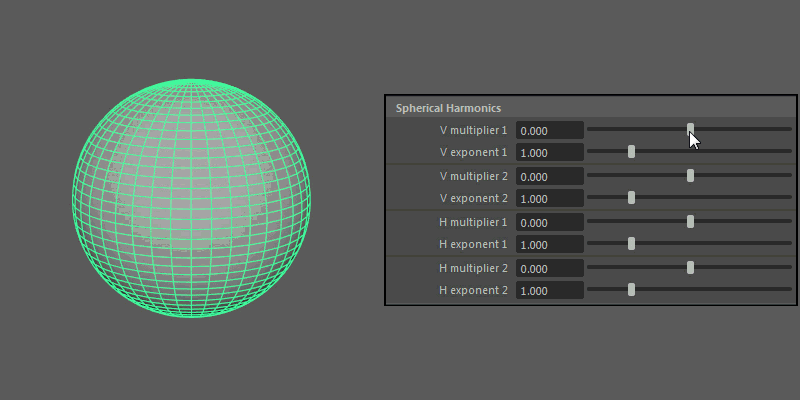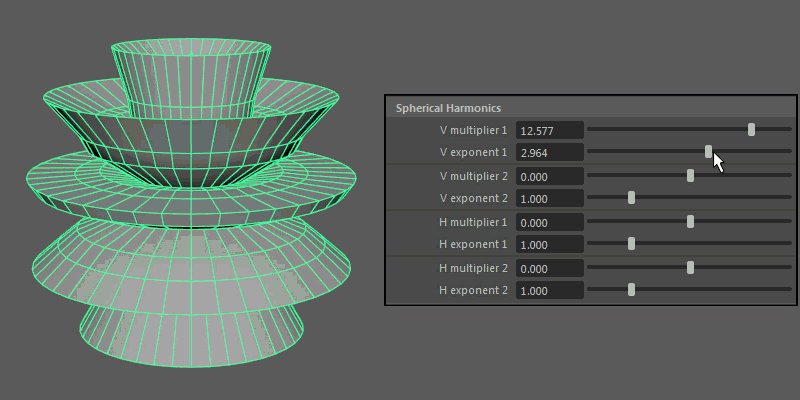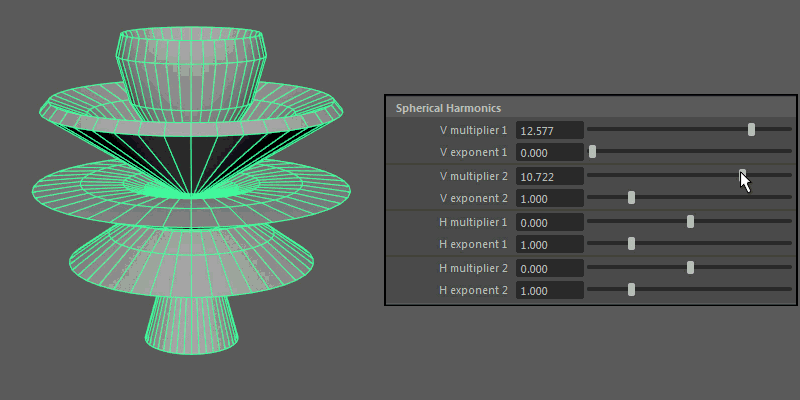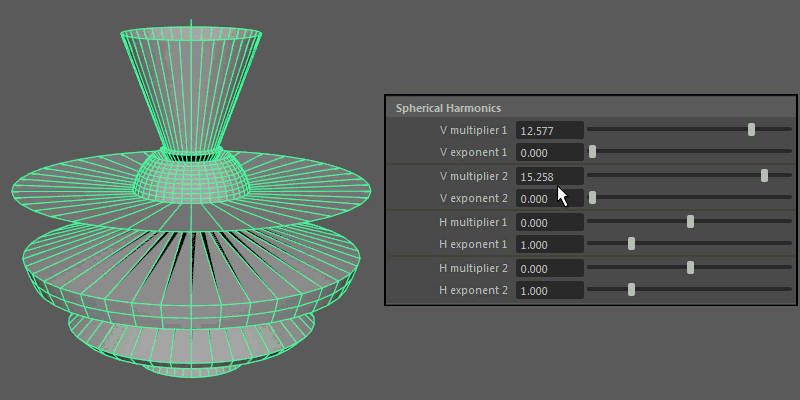
H multiplier, H exponent: Controls the mathematical variables used to determine the shape along the horizontal.
Ultra
Ultra shapes use an algorithm specifically designed to create organic-looking shapes.
Horizontal
Controls the pattern across the ultra shape's latitude
Multiplier 1, Multiplier 2: Controls the main horizontal protrusions from the ultra shape. Both values can exist on the ultra shape at once, and you can blend between them using the Mixer attribute
Exponent 1, Exponent 2, Exponent 3, Exponent 4: Controls the extent of the horizontal extrusions for Multiplier 1 ( Exponent 1 and 2) and Multiplier 2 ( Exponent 3 and 4) respectively.
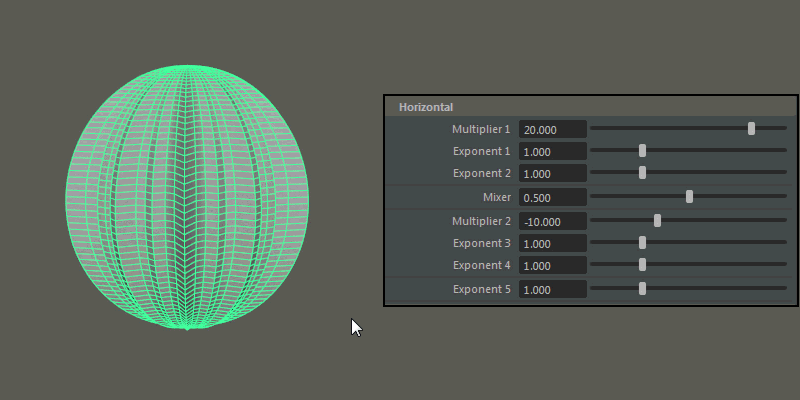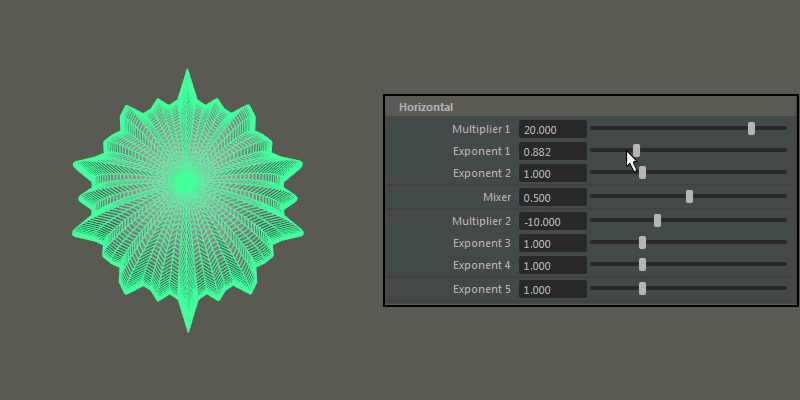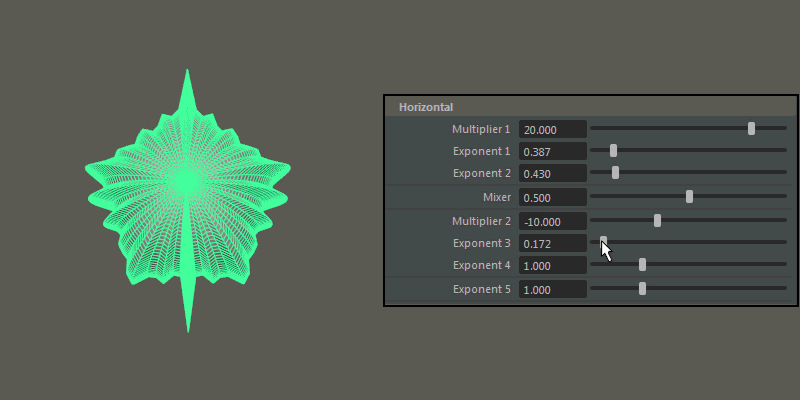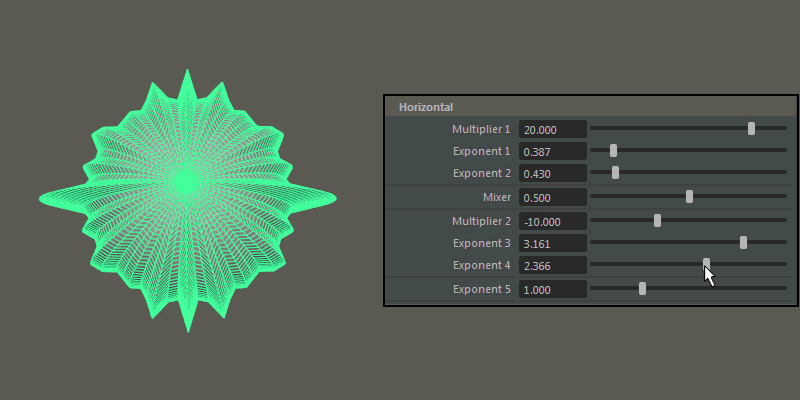
Exponent 5: Controls the overall extent of the horizontal protrusions resulting from the previous Multipliers and Exponents.
Vertical
Controls the pattern across the ultra shape's longitude.
Multiplier 1, Multiplier 2: Controls the main vertical protrusions from the ultra shape. Both values can exist on the ultra shape at once, and you can blend between them using the Mixer attribute (animation link).
Exponent 1, Exponent 2, Exponent 3, Exponent 4: Controls the extent of the vertical extrusions for Multiplier 1 ( Exponent 1 and 2) and Multiplier 2 ( Exponent 3 and 4) respectively (animation link).
Exponent 5: Controls the overall extent of the vertical protrusions resulting from the previous Multipliers and Exponents.
Forums Links
Can't find what you're looking for? Ask the community or share your knowledge.





















